Enterolite nécrosante
20/12/11 22:32
ENTEROCOLITE NECROSANTE
1. cible: préma entre 1 et 3 sem vie
classique touche le préma vers le 11°j de vie car
Touche prématuré ou terme avec terrain prédisposant (hirschprung)
2. Méc: idiopathique (infection + ischémie)
Souffrance fœtale côlon => TD « OK » jusqu'au démarrage de la nutrition au 11° jour
3. Topo: iléon et colon droit
4. Clin:
abdo distendu
résidus gastriques
hematest+
intolerance alimentaire
sepsis
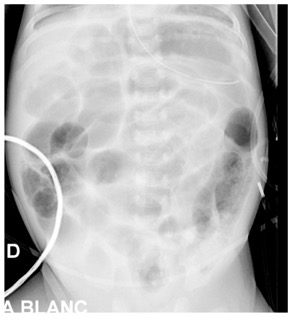
Rx:
1. dilatation focale du tube surtout FID (DD= HIRSCHPRUNG)
2. séparation anses grêle (liquide inter anse)
3. anse grêle dévillosée
4. fixation du pattern gazeux sur clichés successifs
5. pneumatose pariétale: (peut mimer matières mais elles existent rarement chez un préma malade en USI!!)
6. Aéroportie
7. perforation avec pneumopéritoine (seule indic chic ABSOLUE) Rigler sign paroi visible des deux cotés
Evolution temporelle en trois phases
1. distension du segment malade
2. chasse hémorragique: vidange du segment malade alors que le grêle reste dilaté
3. Redilatation avec pneumatose pariétale (US et AAB)
4. Perforation
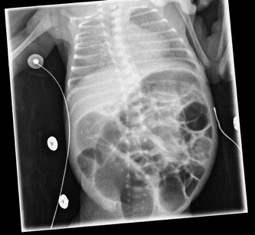
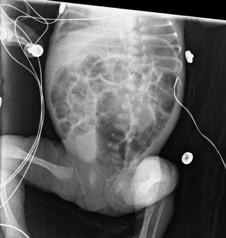
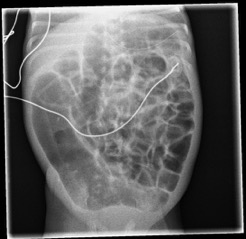
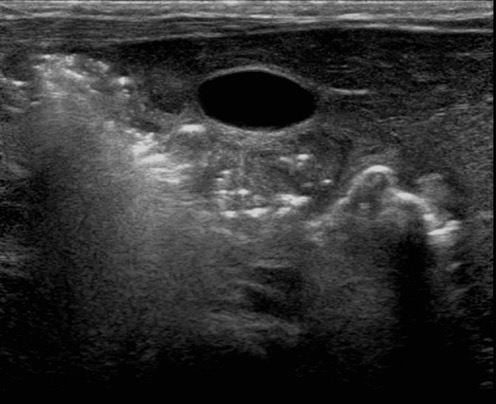
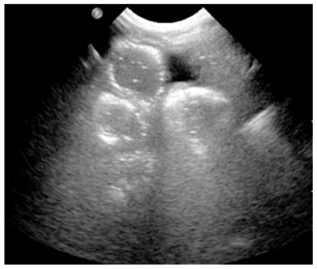
US:
aide chez abdomen peu aéré: montrant paroi épaissie et absence ou augmentation de doppler puis liquide libre en quantité importante
1. Free intraperitoneal gas was identified by the presence of linear or punctuate echogenic foci outside of the bowel with reverberation artifact (Fig. 1).
2. Focal fluid collections were identified as focal locules of fluid with complex echoes within.
3. Bowel wall thickening was considered present when bowel wall thickness was 2.7 mm or greater.
4. Bowel wall thinning was considered present when bowel wall thickness was 1.0 mm or less (Fig. 2).
5. Bowel wall hyperechogenicity was considered present when there was loss of the hypoechogenic muscle layer (“bowel gut signature”) with an overall increase in mural echogenicity.
6. Pneumatosis intestinalis was defined by the presence of punctate echogenic foci within the bowel wall. Reverberation artifact was not required for this diagnosis (Fig. 3).
7. Portal venous gas was defined by the presence of punctate or linear echogenic foci within the portal vessels (Fig. 4).
8. Anechoic free fluid
9. Echogenic free fluid
10. Increased perfusion was determined from review of the color Doppler images. Evaluation was subjective, as above.
11. Absent bowel perfusion was recognized when no flow was seen within a loop of bowel on color Doppler imaging (Fig. 2).
12. Aperistalsis was defined as absence of peristalsis on cine sequences. If cine sequences were not available, the radiologist’s report was reviewed to determine if peristalsis was observed and documented at real-time imaging.
13. Dilated bowel with anechoic contents was defined by the presence of anechoic fluid within bowel whose diameter was equal to or greater than two vertebral body heights (as seen on radiography; this was used as a convenient internal control for size).
pneumatose US :
FOCI hyperUS de la paroi (petites bulles d’air) secouer avec la sonde pour analyser la mobilité
DD : enterocolique nécrosante, maladie de crohn, sepsis, allergie PLV!!!
Perte de la couche hypoUS paroi colique
=> diagnostic par le suivi
PATHO
NORMAL
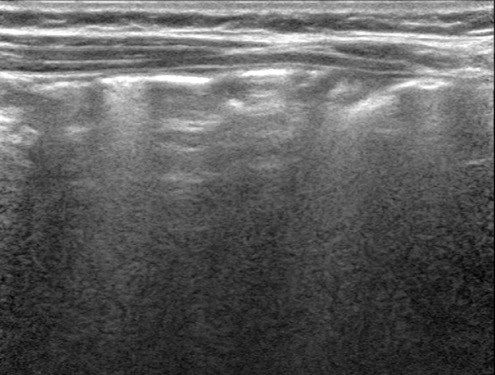
NORMAL
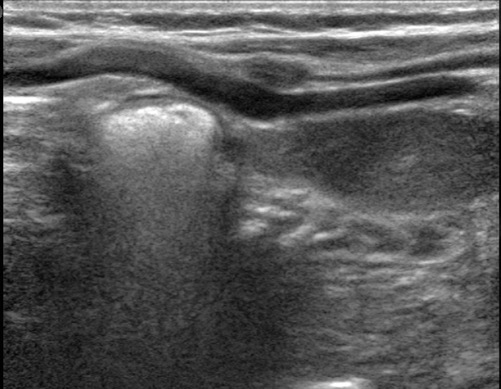
PATHO
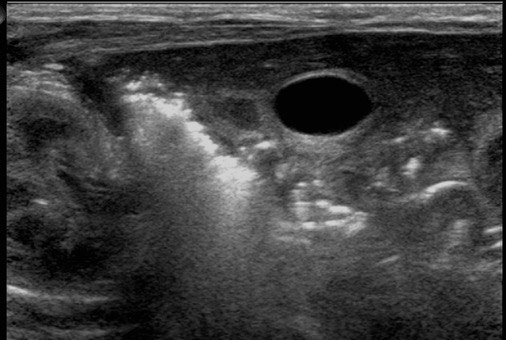
Trt
médical: AB et TPN
Chir: si perfo ou sur base rx-clin
Complic:
sténose postNEC le plus souvent à gauche.
Sténose post inflammatoire peut survenir jusqu'à 6 mois après même si asympto
hyperemie 2aire importante en phase de guérison puis régresse en 3 semaines sauf les zones où sténoses arriveront !
CRP persistant à 4 semaines augmente le risque de sténose
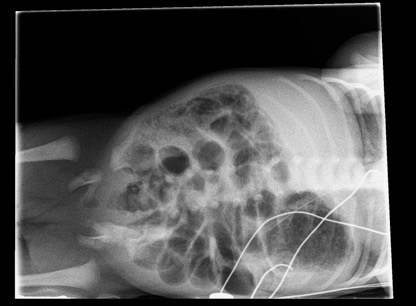
DD ischémie par surdistension et non vasculaire ou infectieux.
Dans ce cas, chercher un hirschprung pancolique
1. cible: préma entre 1 et 3 sem vie
classique touche le préma vers le 11°j de vie car
Touche prématuré ou terme avec terrain prédisposant (hirschprung)
2. Méc: idiopathique (infection + ischémie)
Souffrance fœtale côlon => TD « OK » jusqu'au démarrage de la nutrition au 11° jour
3. Topo: iléon et colon droit
4. Clin:
abdo distendu
résidus gastriques
hematest+
intolerance alimentaire
sepsis
Rx:
1. dilatation focale du tube surtout FID (DD= HIRSCHPRUNG)
2. séparation anses grêle (liquide inter anse)
3. anse grêle dévillosée
4. fixation du pattern gazeux sur clichés successifs
5. pneumatose pariétale: (peut mimer matières mais elles existent rarement chez un préma malade en USI!!)
6. Aéroportie
7. perforation avec pneumopéritoine (seule indic chic ABSOLUE) Rigler sign paroi visible des deux cotés
Evolution temporelle en trois phases
1. distension du segment malade
2. chasse hémorragique: vidange du segment malade alors que le grêle reste dilaté
3. Redilatation avec pneumatose pariétale (US et AAB)
4. Perforation



US:
aide chez abdomen peu aéré: montrant paroi épaissie et absence ou augmentation de doppler puis liquide libre en quantité importante
1. Free intraperitoneal gas was identified by the presence of linear or punctuate echogenic foci outside of the bowel with reverberation artifact (Fig. 1).
2. Focal fluid collections were identified as focal locules of fluid with complex echoes within.
3. Bowel wall thickening was considered present when bowel wall thickness was 2.7 mm or greater.
4. Bowel wall thinning was considered present when bowel wall thickness was 1.0 mm or less (Fig. 2).
5. Bowel wall hyperechogenicity was considered present when there was loss of the hypoechogenic muscle layer (“bowel gut signature”) with an overall increase in mural echogenicity.
6. Pneumatosis intestinalis was defined by the presence of punctate echogenic foci within the bowel wall. Reverberation artifact was not required for this diagnosis (Fig. 3).
7. Portal venous gas was defined by the presence of punctate or linear echogenic foci within the portal vessels (Fig. 4).
8. Anechoic free fluid
9. Echogenic free fluid
10. Increased perfusion was determined from review of the color Doppler images. Evaluation was subjective, as above.
11. Absent bowel perfusion was recognized when no flow was seen within a loop of bowel on color Doppler imaging (Fig. 2).
12. Aperistalsis was defined as absence of peristalsis on cine sequences. If cine sequences were not available, the radiologist’s report was reviewed to determine if peristalsis was observed and documented at real-time imaging.
13. Dilated bowel with anechoic contents was defined by the presence of anechoic fluid within bowel whose diameter was equal to or greater than two vertebral body heights (as seen on radiography; this was used as a convenient internal control for size).
pneumatose US :
FOCI hyperUS de la paroi (petites bulles d’air) secouer avec la sonde pour analyser la mobilité
DD : enterocolique nécrosante, maladie de crohn, sepsis, allergie PLV!!!
Perte de la couche hypoUS paroi colique
=> diagnostic par le suivi
PATHO

NORMAL

NORMAL

PATHO

Trt
médical: AB et TPN
Chir: si perfo ou sur base rx-clin
Complic:
sténose postNEC le plus souvent à gauche.
Sténose post inflammatoire peut survenir jusqu'à 6 mois après même si asympto
hyperemie 2aire importante en phase de guérison puis régresse en 3 semaines sauf les zones où sténoses arriveront !
CRP persistant à 4 semaines augmente le risque de sténose

DD ischémie par surdistension et non vasculaire ou infectieux.
Dans ce cas, chercher un hirschprung pancolique

